PostgreSQL CREATE DATABASE
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL CREATE DATABASE statement to create new databases in the PostgreSQL server.
Introduction to PostgreSQL CREATE DATABASE statement
In PostgreSQL, a database is a collection of related data, which serves as a container for tables, indexes, views, and other database objects.
To create a new database, you use the CREATE DATABASE statement.
Here’s the basic syntax of the CREATE DATABASE statement:
CREATE DATABASE database_name
WITH
[OWNER = role_name]
[TEMPLATE = template]
[ENCODING = encoding]
[LC_COLLATE = collate]
[LC_CTYPE = ctype]
[TABLESPACE = tablespace_name]
[ALLOW_CONNECTIONS = true | false]
[CONNECTION LIMIT = max_concurrent_connection]
[IS_TEMPLATE = true | false ];In this syntax:
- First, specify the name of the new database that you want to create after the
CREATE DATABASEkeywords. The database name must be unique in the PostgreSQL server. If you attempt to create a database whose name already exists, PostgreSQL will issue an error. - Then, use one or more parameters for the new database.
Parameters
OWNER
Assign a role that will be the owner of the database. If you omit the OWNER option, the database owner is the role you use to execute the CREATE DATABASE statement.
TEMPLATE
Specify the template database for the new database. PostgreSQL uses the template1 database as the default template database if you don’t explicitly specify the template database.
ENCODING
Determine the character set for the new database.
LC_COLLATE
Specify the collation order (LC_COLLATE) that the new database will use. This parameter affects the sort order of strings in queries that contain the ORDER BY clause. It defaults to the LC_COLLATE of the template database.
LC_CTYPE
Specify the character classification that the new database will use. It affects the classification of characters such as lower, upper, and digit. It defaults to the LC_CTYPE of the template database
TABLESPACE
Specify the tablespace name for the new database. The default is the tablespace of the template database.
CONNECTION LIMIT
Specify the maximum concurrent connections to the new database. The default is -1 which means unlimited. This parameter can be useful in shared hosting environments where you can configure the maximum concurrent connections for a particular database.
ALLOW_CONNECTIONS
The allow_connections parameter is a boolean value. If it is false, you cannot connect to the database.
TABLESPACE
Specify the tablespace that the new database will use. It defaults to the tablespace of the template database.
IS_TEMPLATE
If the IS_TEMPLATE is true, any user with the CREATEDB privilege can clone it. If false, only superusers or the database owner can clone it.
To execute the CREATE DATABASE statement, you need to have a superuser role or a special CREATEDB privilege.
PostgreSQL CREATE DATABASE examples
Let’s explore some examples of using the CREATE DATABASE statement.
1) Create a database with default parameters
First, open the Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on Unix-like systems and connect to the PostgreSQL server:
psql -U postgresSecond, execute the CREATE DATABASE statement to a new database with default parameters:
CREATE DATABASE sales;Output:
CREATE DATABASEPostgreSQL will create a new database called sales that has default parameters from the default template database (template1).
Third, show all the databases using the \l command:
\lOutput:
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Locale Provider | Collate | Ctype | ICU Locale | ICU Rules | Access privileges
-----------+----------+----------+-----------------+----------------------------+----------------------------+------------+-----------+-----------------------
dvdrental | postgres | UTF8 | libc | English_United States.1252 | English_United States.1252 | | |
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | libc | English_United States.1252 | English_United States.1252 | | |
tempdb | postgres | UTF8 | libc | English_United States.1252 | English_United States.1252 | | |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | libc | English_United States.1252 | English_United States.1252 | | | =c/postgres +
| | | | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | libc | English_United States.1252 | English_United States.1252 | | | =c/postgres +
| | | | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
(5 rows)Alternatively, you can retrieve the database names from the pg_database view:
SELECT datname FROM pg_database;Output:
datname
-----------
postgres
dvdrental
template1
template0
tempdb
sales
(6 rows)2) Create a database with options
The following example uses the CREATE DATABASE statement to create a database named hr with some parameters:
CREATE DATABASE hr
WITH
ENCODING = 'UTF8'
CONNECTION LIMIT = 100;This statement creates a database called hr with the encoding UTF8 and the number of concurrent connections to the database is 100.
3) Creating a new database using pgAdmin
The pgAdmin tool provides an intuitive interface for creating a new database.
First, connect to the PostgreSQL database server using pgAdmin.
Second, right-click the Databases node and select Create > Database… menu item
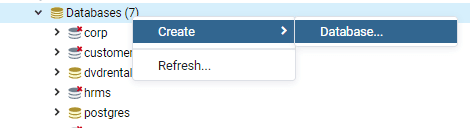 It will show a dialog to enter detailed information on the new database.
It will show a dialog to enter detailed information on the new database.
Third, enter the name of the database and select an owner in the general tab.
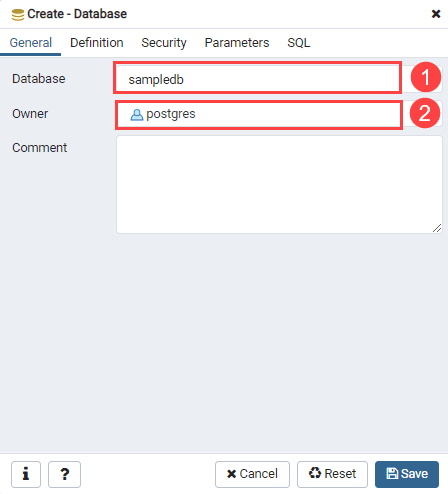 In this example, we create a new database called
In this example, we create a new database called sampledb and owner postgres.
Fourth, select the Definition tab to set the properties for the database:
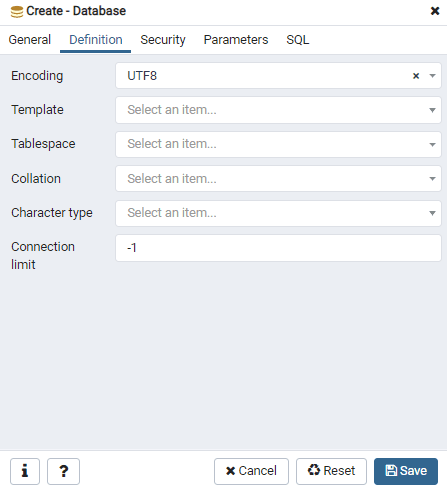 In the Definition tab, you can select the encoding, a template, tablespace, collation, character type, and connection limit.
In the Definition tab, you can select the encoding, a template, tablespace, collation, character type, and connection limit.
The Security tab allows you to define security labels and assign privileges. The Privileges tab allows you to assign privileges to a role.
Fifth, click the SQL tab to view the generated SQL statement that will execute.
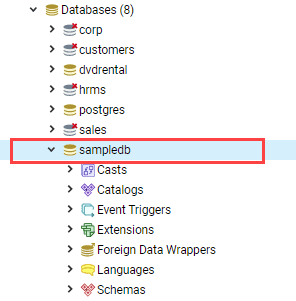
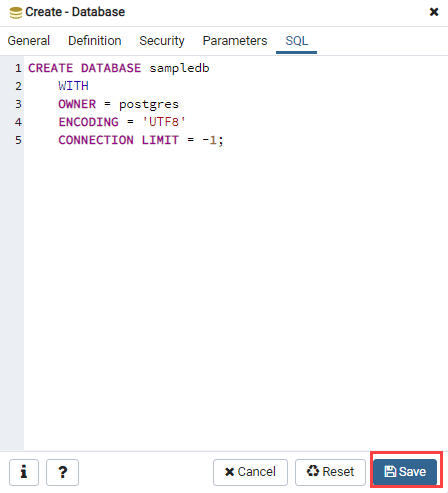 Finally, click the Save button to create the
Finally, click the Save button to create the sampledb database. You will see the sampledb listed on the database list:
Summary
- Use the
CREATE DATABASEstatement to create a new database.